Weekly Summary – September 1, 2025
This week marked a significant milestone with the formal publication of the Ouroboros Leios CIP proposal, complemented by the release of the second comprehensive technical report and extensive network performance analysis. The team successfully delivered the definitive protocol specification and supporting evidence to the Cardano Foundation for formal review.
Major milestone achievement
CIP proposal publication
The team published the Ouroboros Leios CIP proposal to the Cardano Foundation CIPs repository, representing the culmination of extensive research, analysis, and specification development. The proposal has been submitted for formal review and is pending assignment of a CIP number at the next CIP meeting. This submission provides the definitive technical specification for the proposed Leios protocol implementation, establishing the foundation for community review and potential integration into the Cardano ecosystem.
Second technical report release
The team completed and released the second technical report, capturing comprehensive modeling, simulation, and analysis findings from March to August 2025. This substantial document covers network protocols, threat model analysis, simulation experiments, test network topologies, empirical Cardano network measurements, analytic studies of proposed Leios behavior and performance, and extensive technical observations. The report provides provisional findings and conclusions acknowledging the evolving nature of the protocol design during the study period.
Network infrastructure analysis
Inter-datacenter bandwidth measurements
The team conducted extensive inter-datacenter bandwidth measurements using iperf3 for bidirectional testing between locations across North America and Europe. The comprehensive analysis examined bandwidth between OVH, AWS, and CenturyLink infrastructure across multiple geographic regions, establishing empirical baselines for network performance expectations in distributed deployment scenarios.
Key findings from the bandwidth analysis indicate that 100 Mbps represents a conservative lower bound for inter-datacenter connectivity, with significant variation based on geographic distance and infrastructure provider combinations. The measurements revealed bandwidth ranges from 95 Mbps (CenturyLink Colorado to OVH Canada) to 973 Mbps (AWS Oregon to OVH Oregon), providing critical input for proposed Leios deployment planning and parameter optimization.
Network degradation resilience analysis
The team completed comprehensive network degradation experiments, examining proposed Leios behavior under severely constrained network topologies. The analysis systematically reduced network connections by up to 87% from original mainnet-like topology configurations, testing protocol resilience under extreme network degradation scenarios.
The degradation experiments demonstrated that the proposed Leios protocol continues to operate correctly even when 87% of network connections are lost, with the network diameter increasing from 5 to 8 hops and the average connections per node dropping from 23.5 to 6.0. The protocol maintained functionality under both honest scenarios and adversarial conditions where attackers delay transaction and EB releases, indicating robust operation under degraded network conditions.
Validation performance analysis
Quantile regression analysis
The team extended ledger operation analysis with comprehensive quantile regressions at 50th, 95th, and 99th percentiles for ledger 'apply' and 'reapply' operations. This analysis addressed concerns about validation time interference between EB reapplication and Praos block release timing.
The quantile analysis provides predictions for full EBs with varying Plutus script intensities, demonstrating that 'apply' operations occur distributed across multiple slots and computational threads. At the same time, 'reapply' operations must complete before new reference blocks (RBs) and EBs can build upon newly certified EBs.
CIP documentation enhancements
Updated figures and regression validation
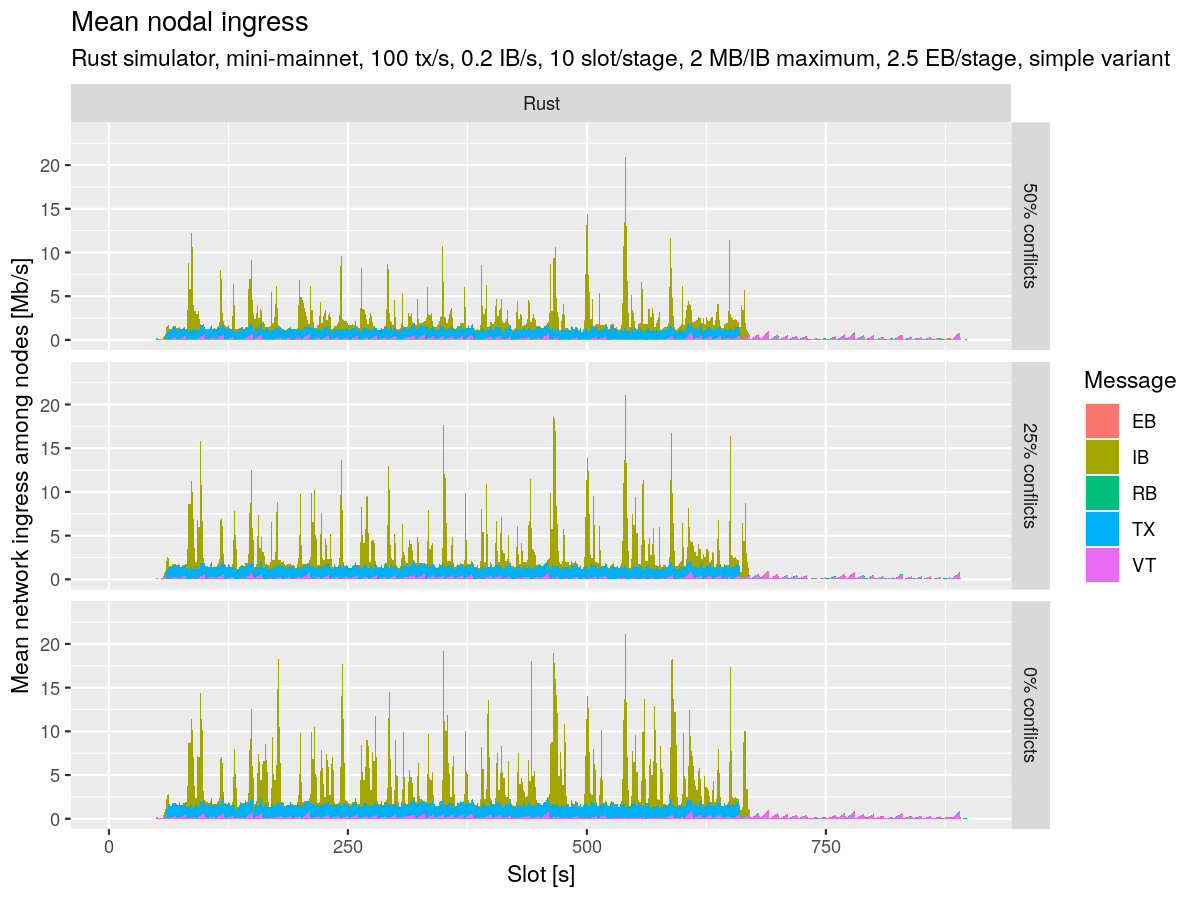
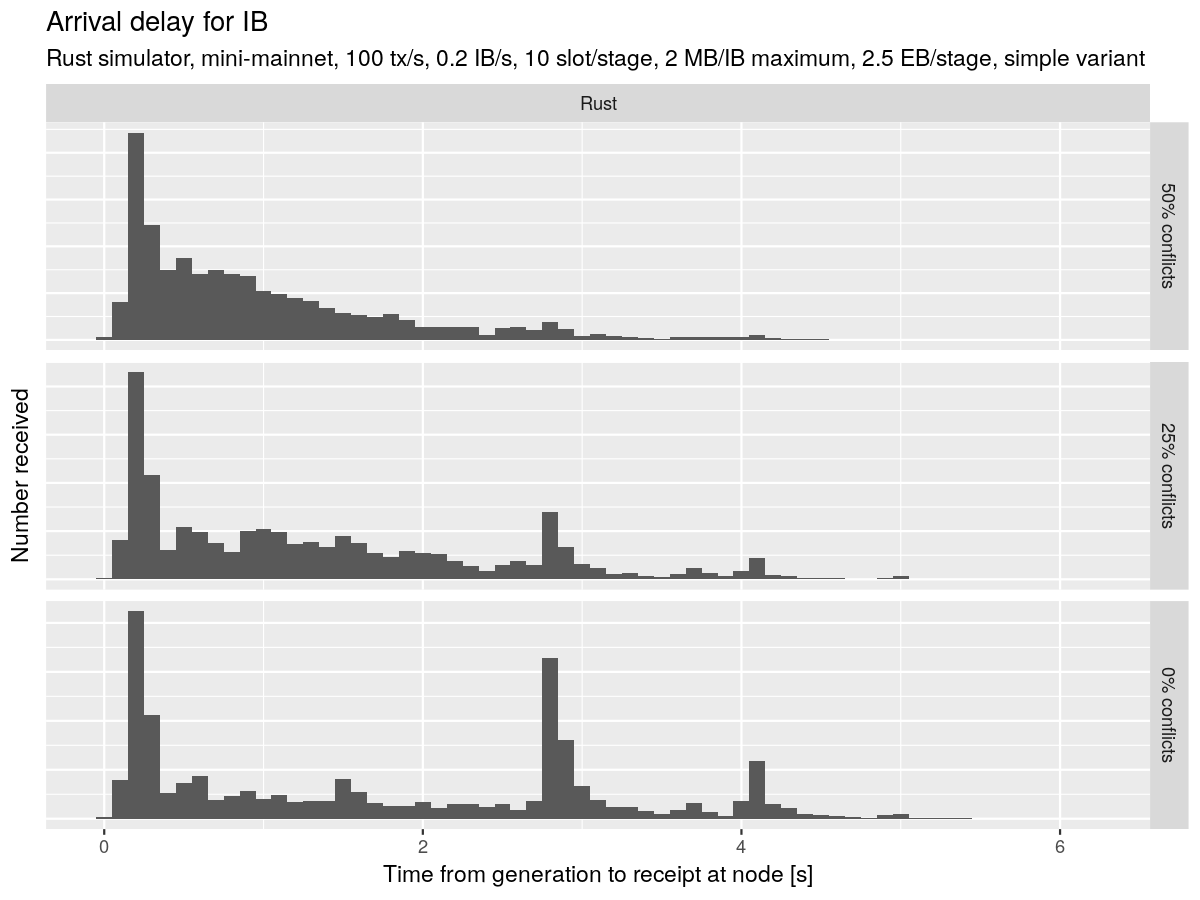
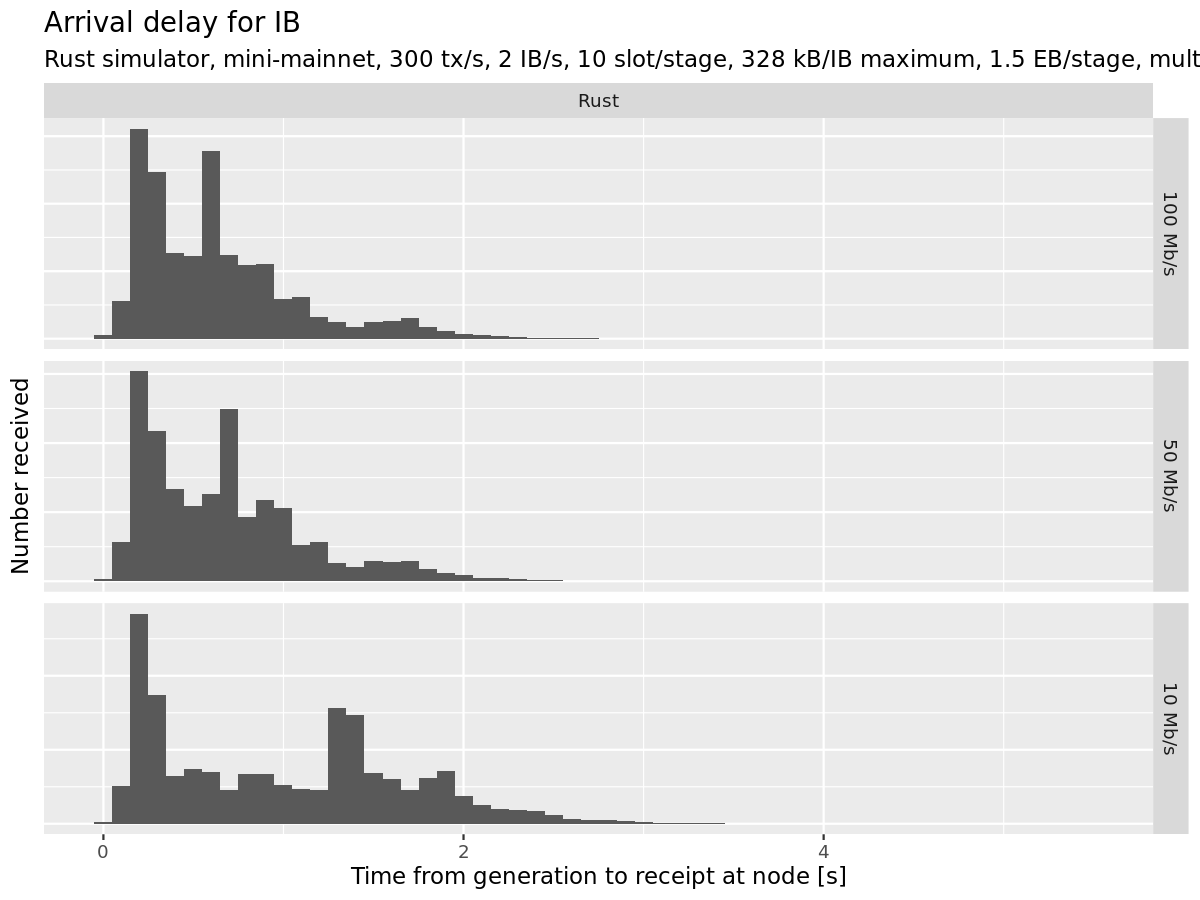
The team regenerated comprehensive figures for CIP inclusion using the upgraded sim-cli version 1.3.0, which included updated diffusion and voting duration configurations. The regression experiment analysis compared performance across simulator versions, revealing minimal discrepancies but slightly reduced performance with version 1.3.0 compared to previous versions.
Next steps
- Monitor CIP review process and respond to community feedback
- Continue protocol parameter refinement based on ongoing analysis
- Extend network analysis to additional deployment scenarios
- Develop implementation guidelines based on technical report findings.