Weekly Summary – April 21, 2025
This week, the Leios team made significant progress in protocol development, focusing on simulation improvements, network protocol design, and economic analysis. The team completed extensive simulations across 648 scenarios, implemented new mini-protocols for Leios diffusion, and conducted important economic analysis regarding future reward sustainability.
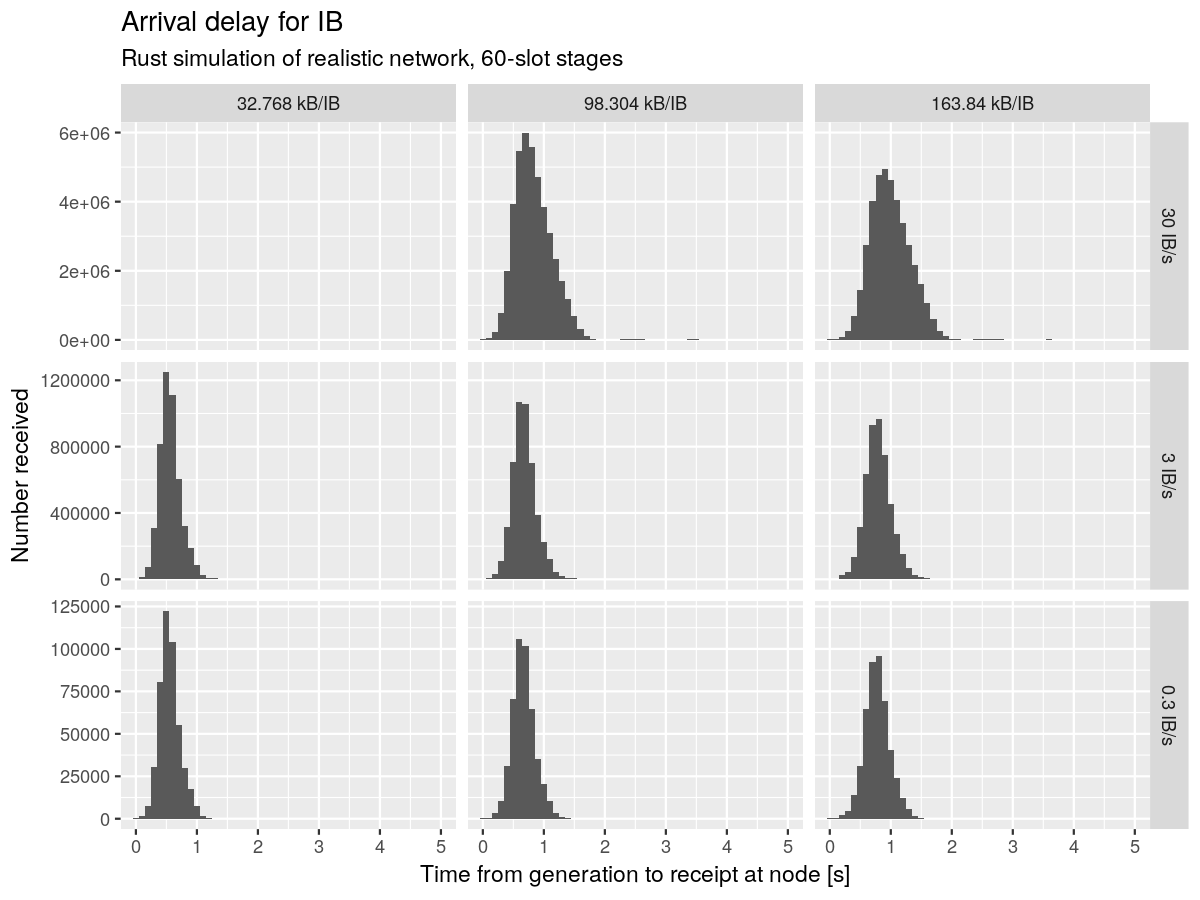
Simulation and analysis
- Completed comprehensive simulation of 648 scenarios for Full and Short Leios at tag
leios-2025w16 - Generated new analysis outputs:
- Network, disk, and CPU resource usage summaries
- Interactive "Leios graph" visualization showing transaction, IB, EB, RB, and vote linkages
- Key findings from simulations:
- Strong agreement between Rust and Haskell implementations
- Haskell simulation shows network congestion at 16 IB/s
- Rust simulation demonstrates higher CPU usage at elevated IB rates
- Identified voting certification issues in Rust implementation.
Protocol development
Haskell implementation
- Completed first draft of new mini-protocols for Leios diffusion:
- IB-relay, EB-relay, Vote-relay for header diffusion
- IB-fetch, EB-fetch for body diffusion
- CatchUp protocol for historical blocks
- Renamed
short-leioscommand toleiosto reflect full variant support.
Rust implementation
- Fixed conformance with shared trace format
- Resolved voting logic bug affecting EB certification
- Updated visualization system for documentation site integration.
Economic analysis
The team conducted a detailed analysis of transaction lifecycle and future reward sustainability:
- Analyzed seven stages of Full Leios transaction processing
- Identified optimal stage lengths and shard configurations
- Estimated two-minute average delay from transaction submission to RB reference
- Projected future IB rates needed to maintain current reward levels:
- Current Reserve depletion rate: 12.8% per year
- Required IB rates increase from 0.008 to 0.634 blocks/slot by 2035
- Analysis assumes constant fee-related protocol parameters.
Next steps
- Translate transaction lifecycle model to Delta QSD for network effects analysis
- Compare model results with Rust simulator output
- Develop memory-pool and ledger variant models
- Continue investigation of voting certification issues in Rust implementation.