Weekly Summary – March 10, 2025
· 4 min read
This week, the Leios team made significant progress in simulation capabilities, with a successful comparison of Rust and Haskell simulations across 90 scenarios. A mainnet-scale analysis of Leios on a realistic 3,000-node network revealed unexpected performance benefits from network topology. Insights from sharding performance analysis provided important optimization strategies. Finally, the team refined both simulation implementations for greater realism and comparability, while the formal methods team developed initial trace verification tools for Short Leios.
Simulation comparison
- Compared 90 scenarios between Rust and Haskell simulations at tag
leios-2025w11 - Recent fixes and adjustments enabled meaningful comparison between simulations
- Identified issues requiring further investigation.
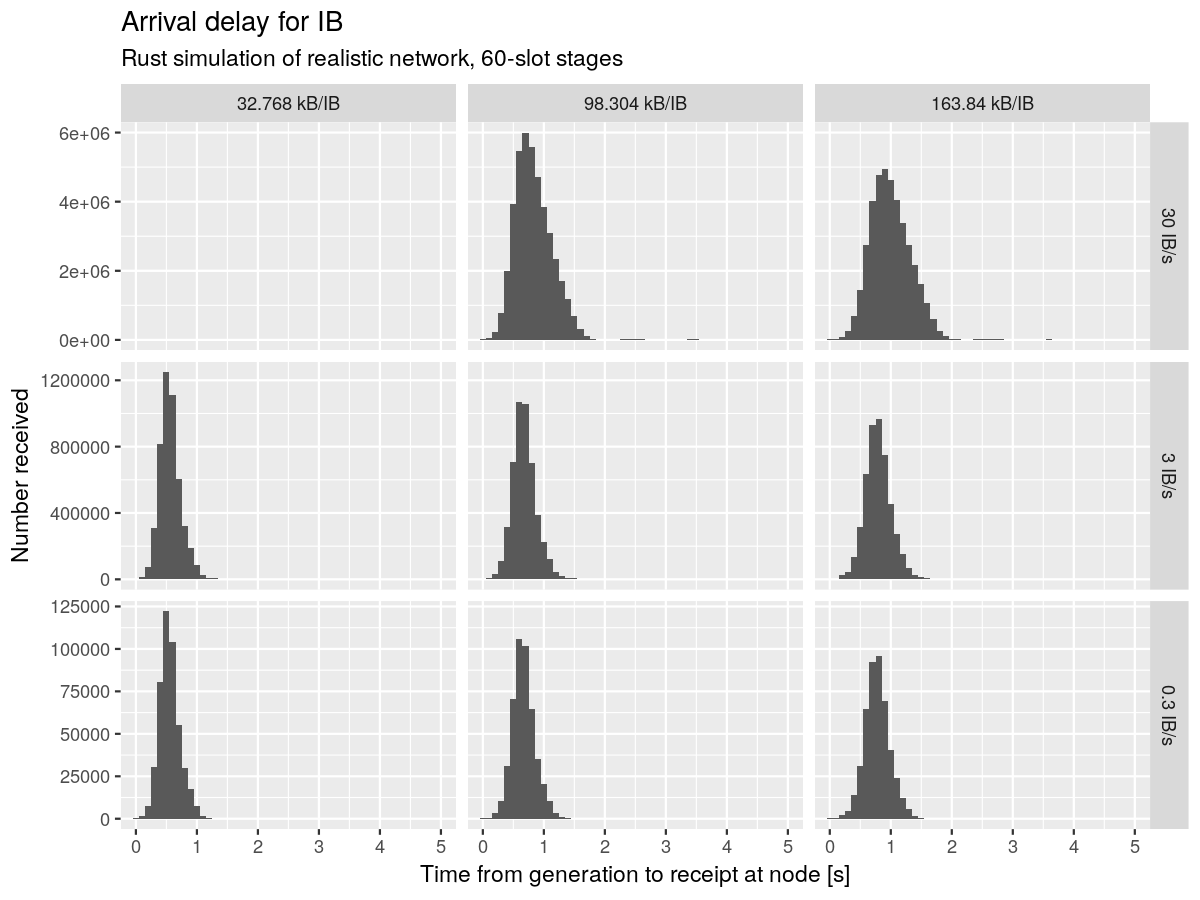
Analysis of mainnet-scale simulation
- Completed the first analysis of Leios on a mainnet-scale network simulation using the Rust simulator
- Discovered that a 3,000-node mainnet-scale network transports IBs faster than an artificial 100-node network
- Identified 'shortcut' edges in larger networks as a likely factor in the improved transport speed.
Performance analysis of sharding
- Created computational models to analyze the relationship between the fraction of shards without an IB and the expected number of extra IBs
- Evaluated performance characteristics of the simplest sharding scheme.
Haskell simulation
- Fixed a bug in the relay protocol that prevented full diffusion of votes
- Adjusted the priority of certified EBs for inclusion in RBs
- Added support for an output log format that shares a common subset with the Rust simulator
- Analyzed TCP realism in comparison to idealized diffusion:
- Discovered that higher IB rates and sizes improve diffusion times
- Identified ledger state access as a significant source of latency.
Rust simulation
- Expanded logs to include total IB size and parent ID of RBs
- Implemented the same EB selection strategy as in the Haskell simulation
- Added validation of IB headers before propagation to neighbors
- Investigating lower congestion in the Rust simulation compared to Haskell.
Formal methods
- Developed the initial trace verifier for Short Leios simulation traces in
leios-trace-verifier.
Research
- Progressing on ledger design by exploring options and trade-offs
- Analyzing how concurrent input blocks in Leios create unique ledger-level challenges not present in Praos
- Evaluating approaches that balance multiple properties, including:
- Conflict avoidance in the blockchain
- Guaranteed fee payment for block producers
- Transaction eligibility and inclusion speed
- User experience regarding fee payment
- Investigating sharding-based solutions with various optimization strategies
- Planning to share more detailed findings at Leios public meeting by the end of March
- Targeting a comprehensive recommendation for implementors by the end of April.
From Short Leios to Full Leios
- Planning the simulation roadmap for transitioning from Short Leios (currently implemented) to Full Leios
- Developing implementation guidelines for simulators to incorporate the pipeline referencing scheme specified in the papers
- Identifying key components needed to simulate the complete ledger inclusion guarantees of Full Leios.